Introduction
Data scattered across multiple systems, platforms, and formats creates significant challenges for modern organizations. When customer information sits in one database, sales data in another, and analytics tools can’t access either, businesses lose valuable opportunities for insight and growth.
Data linkers solve this fundamental problem by creating bridges between disparate data sources. These powerful tools enable organizations to connect, integrate, and synchronize information across their entire technology ecosystem without the need for complex custom coding or expensive enterprise solutions.
This comprehensive guide explores everything you need to know about data linkers, from their core functionality to implementation best practices. Whether you’re a data analyst struggling with siloed information or an IT professional looking to streamline your organization’s data architecture, understanding data linkers will transform how you approach data connectivity challenges.
What Are Data Linkers?
Data linkers are software tools designed to establish connections between different data sources, enabling seamless information flow across systems. They act as intermediaries that can read, translate, and transfer data between applications, databases, APIs, and file formats that might otherwise be incompatible.
Unlike traditional data integration solutions that often require extensive programming knowledge, modern data linkers provide user-friendly interfaces that allow both technical and non-technical users to create data connections. They handle the complex technical aspects of data formatting, protocol translation, and connection management behind the scenes.
The primary function of data linkers extends beyond simple data movement. They ensure data consistency, handle error management, and provide monitoring capabilities to maintain reliable data flows. This makes them essential tools for organizations dealing with multiple software applications, cloud services, and data formats.
Understanding the Sub-layers of Data Link Layer
Data linkers operate within a structured framework that mirrors the data link layer of network communications. This layer contains two critical sub-layers that ensure reliable data transmission:
Logical Link Control (LLC) Sub-layer
The LLC sub-layer manages the logical aspects of data linking. It handles flow control, error detection, and maintains the integrity of data connections. When data linkers establish connections between sources, the LLC functionality ensures that information transfers reliably and maintains its structure throughout the process.
This sub-layer also manages multiplexing, allowing a single data linker to handle multiple simultaneous connections without interference. For organizations managing numerous data sources, this capability proves essential for maintaining efficient operations.
Media Access Control (MAC) Sub-layer
The MAC sub-layer focuses on the physical aspects of data transmission. It manages how data linkers access different systems, handles addressing protocols, and controls the timing of data transfers. This ensures that data flows don’t overwhelm target systems and that connections remain stable under varying load conditions.
Understanding these sub-layers helps organizations choose data linkers that provide the appropriate level of control and reliability for their specific use cases.
Benefits of Using Data Linkers
Data linkers deliver substantial advantages that extend far beyond simple data connectivity. Organizations implementing these tools typically experience improved operational efficiency, better decision-making capabilities, and reduced technical overhead.
Enhanced Data Accessibility
Data linkers eliminate information silos by creating direct pathways between previously disconnected systems. Teams can access the information they need without waiting for IT support or manually exporting and importing files. This immediate accessibility accelerates project timelines and improves productivity across departments.
Streamlined Workflows
Automated data flows reduce manual intervention and minimize the risk of human error. When data moves automatically between systems, teams spend less time on routine data management tasks and more time on analysis and strategic activities. This workflow optimization often results in significant time savings and improved accuracy.
Real-time Data Synchronization
Modern data linkers support real-time or near-real-time data synchronization, ensuring that all systems maintain current information. This capability proves particularly valuable for customer service teams, sales departments, and operational systems that require up-to-date data for effective decision-making.
Cost Reduction
By eliminating the need for custom integration development, data linkers reduce both initial implementation costs and ongoing maintenance expenses. Organizations can achieve complex data connectivity without hiring specialized developers or investing in expensive enterprise integration platforms.
Transform Your Data Link Strategy with Seers
Implementing an effective data linking strategy requires careful planning and the right tools. Seers provides comprehensive data connectivity solutions that simplify the process of linking disparate data sources while maintaining security and compliance standards.
Seers’ data linking platform offers intuitive visual interfaces that allow users to create complex data flows without programming knowledge. The platform supports hundreds of pre-built connectors for popular business applications, databases, and cloud services, significantly reducing implementation time.
The platform also provides robust monitoring and error handling capabilities, ensuring that data flows remain reliable and any issues are quickly identified and resolved. This reliability proves essential for organizations that depend on continuous data availability for their operations.
How Data Linkers Work
Data linkers operate through a systematic process that involves discovery, connection establishment, data mapping, and ongoing synchronization. Understanding this process helps organizations plan their implementation and troubleshoot potential issues.
Data Source Discovery
The process begins with identifying and cataloging available data sources. Modern data linkers can automatically discover databases, applications, and file systems within an organization’s network. They analyze connection protocols, data formats, and access requirements to determine how best to establish connections.
Connection Establishment
Once data sources are identified, data linkers establish secure connections using appropriate protocols and authentication methods. They handle the technical complexities of different connection types, from database connections to API integrations and file system access.
Data Mapping and Transformation
Data linkers analyze the structure and format of source data and map it to target systems. This process includes data type conversion, field mapping, and format transformation to ensure compatibility between different systems. Advanced data linkers provide visual mapping interfaces that simplify this process for non-technical users.
Ongoing Synchronization
After initial setup, data linkers maintain continuous or scheduled synchronization between connected systems. They monitor for changes in source data and propagate those changes to target systems according to predefined rules and schedules.
Use Cases Across Industries
Data linkers find applications across numerous industries and scenarios, each with specific requirements and challenges.
Healthcare Systems Integration
Healthcare organizations use data linkers to connect electronic health records, billing systems, laboratory information systems, and patient management platforms. This integration enables comprehensive patient care while maintaining compliance with healthcare data regulations.
Retail and E-commerce
Retailers leverage data linkers to synchronize inventory information across online platforms, point-of-sale systems, and warehouse management systems. This ensures accurate stock levels and prevents overselling while providing customers with real-time availability information.
Financial Services
Financial institutions use data linkers to connect trading systems, risk management platforms, compliance databases, and customer relationship management systems. This integration provides comprehensive views of customer relationships and enables better risk assessment and regulatory reporting.
Manufacturing Operations
Manufacturing companies implement data linkers to connect production systems, quality management databases, supply chain platforms, and enterprise resource planning systems. This integration provides visibility into entire production processes and enables predictive maintenance and quality control.
Best Practices for Implementation
Successful data linker implementation requires careful planning and adherence to established best practices that ensure reliability, security, and scalability.
Start with Clear Objectives
Define specific goals for data linking initiatives before beginning implementation. Understanding what data needs to move between which systems and how it will be used helps guide tool selection and configuration decisions.
Prioritize Data Quality
Implement data validation and cleansing processes to ensure that only high-quality information flows between systems. Poor data quality can propagate errors across multiple systems and undermine the value of data linking initiatives.
Establish Monitoring and Alerting
Configure comprehensive monitoring to track data flow performance, error rates, and system health. Proactive monitoring enables quick identification and resolution of issues before they impact business operations.
Plan for Scalability
Choose data linking solutions that can grow with organizational needs. Consider future data sources, increasing data volumes, and expanding user requirements when making platform decisions.
Implement Security Controls
Ensure that data linkers maintain appropriate security controls, including encryption, access controls, and audit logging. Data in transit between systems must remain protected according to organizational security policies and regulatory requirements.
Future Trends in Data Linking Technology
The data linking landscape continues evolving rapidly, driven by advances in artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and data management practices.
Artificial Intelligence Integration
AI-powered data linkers will provide smarter data mapping suggestions, automatic error correction, and predictive maintenance capabilities. Machine learning algorithms will optimize data flows and identify patterns that improve overall system performance.
Cloud-Native Solutions
Cloud-native data linkers will offer improved scalability, reduced infrastructure requirements, and better integration with cloud-based applications and services. These solutions will support hybrid and multi-cloud environments more effectively.
Real-Time Processing Capabilities
Enhanced real-time processing capabilities will enable immediate data synchronization and event-driven data flows. This will support use cases that require instantaneous data updates across multiple systems.
Low-Code and No-Code Interfaces
Increasingly sophisticated visual interfaces will make data linking accessible to business users without technical backgrounds. These interfaces will provide drag-and-drop functionality for complex data integration scenarios.
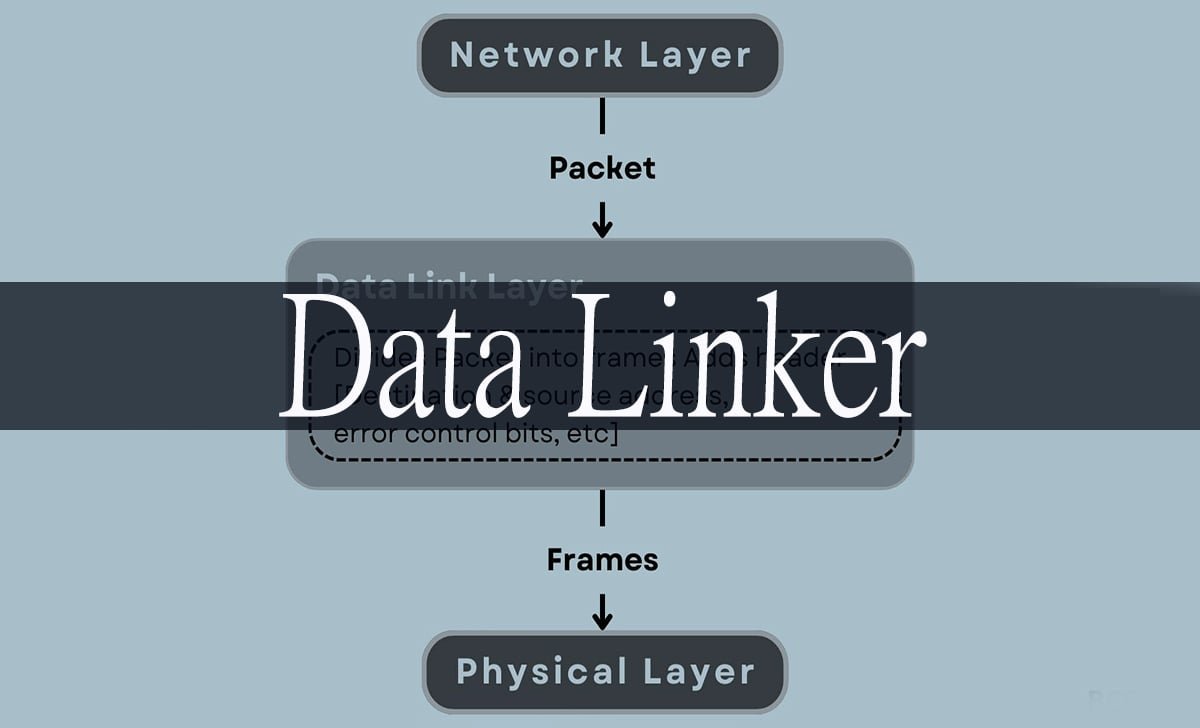
Functions of the Data Link Layer
The data link layer performs several critical functions that ensure reliable data transmission between connected systems. Understanding these functions helps organizations appreciate the complexity that data linkers manage automatically.
Frame Synchronization
Data linkers establish and maintain frame boundaries to ensure that receiving systems can properly interpret incoming data. This synchronization prevents data corruption and ensures accurate information transfer.
Error Detection and Correction
Built-in error detection mechanisms identify transmission errors and either request retransmission or apply correction algorithms. This functionality maintains data integrity even when network conditions are less than optimal.
Flow Control
Flow control mechanisms prevent fast-sending systems from overwhelming slower receiving systems. Data linkers implement buffering and pacing controls to optimize data transfer rates for all connected systems.
Access Control
Data linkers manage access to shared communication channels and ensure that multiple data flows don’t interfere with each other. This coordination becomes critical in environments with numerous concurrent data transfers.
Protocols in Data Link Layer
Data linkers support numerous protocols that enable communication between different types of systems and networks. Understanding these protocols helps organizations choose appropriate solutions for their specific environments.
Ethernet Protocols
Ethernet remains the foundation for many data linking scenarios, particularly in local area networks. Data linkers must handle various Ethernet standards and ensure compatibility across different network segments.
Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP)
PPP enables direct connections between systems and provides authentication and error detection capabilities. Data linkers use PPP for secure point-to-point data transfers between specific systems.
Frame Relay and HDLC
These protocols support wide area network connections and provide reliable data transfer over longer distances. Data linkers implement these protocols when connecting systems across multiple geographic locations.
Wireless Protocols
Modern data linkers support various wireless protocols, including Wi-Fi standards and cellular communications, enabling data connectivity in mobile and remote environments.
Frequently Asked Questions
What’s the difference between data linkers and traditional ETL tools?
Data linkers focus on creating ongoing connections and real-time data flows between systems, while ETL tools typically perform batch processing for data warehousing scenarios. Data linkers are generally easier to implement and maintain for operational data integration needs.
Can data linkers handle large volumes of data?
Modern data linkers are designed to handle substantial data volumes through optimized processing engines and scalable architectures. However, specific capacity depends on the chosen solution and infrastructure configuration.
How do data linkers ensure data security during transmission?
Data linkers implement multiple security layers including encryption, authentication, access controls, and audit logging. They support various security protocols and can integrate with organizational security frameworks.
What happens if a data linker connection fails?
Most data linkers include error handling and recovery mechanisms that can retry failed connections, queue data for later transmission, and alert administrators to connection issues. Advanced solutions provide automatic failover capabilities.
Do data linkers require programming knowledge to implement?
Many modern data linkers provide visual interfaces that require minimal programming knowledge. However, complex scenarios may benefit from technical expertise to optimize performance and handle specialized requirements.
Maximizing Your Data Connectivity Strategy
Data linkers represent a fundamental shift in how organizations approach data connectivity challenges. By simplifying the process of connecting disparate systems and enabling reliable data flows, these tools unlock the full potential of organizational data assets.
Success with data linkers requires thoughtful planning, appropriate tool selection, and adherence to implementation best practices. Organizations that invest in comprehensive data linking strategies position themselves to respond quickly to changing business requirements and leverage data for competitive advantage.
The future of data linking promises even greater capabilities, with AI-driven optimization and cloud-native architectures making data connectivity more accessible and powerful than ever before. Organizations that begin building their data linking capabilities now will be well-positioned to capitalize on these emerging opportunities.
Meta data
Meta title
Data Linkers Guide: Connect & Integrate Your Data Sources
Meta description
Learn how data linkers seamlessly connect disparate systems. Discover benefits, implementation best practices, and future trends in data connectivity.