Introduction
In today’s connected world, almost everything we do online relies on smooth, reliable communication between devices. Whether you’re streaming videos, sending emails, or playing online games, two key protocols manage how data travels across networks: TCP and UDP. While they may sound technical and intimidating, understanding them is simpler than you think. Think of TCP and UDP as different ways of sending messages each with its strengths and weaknesses. In this guide, we’ll break them down in a friendly, easy-to-understand way, helping you grasp why these protocols are crucial for your digital life.
What is TCP?
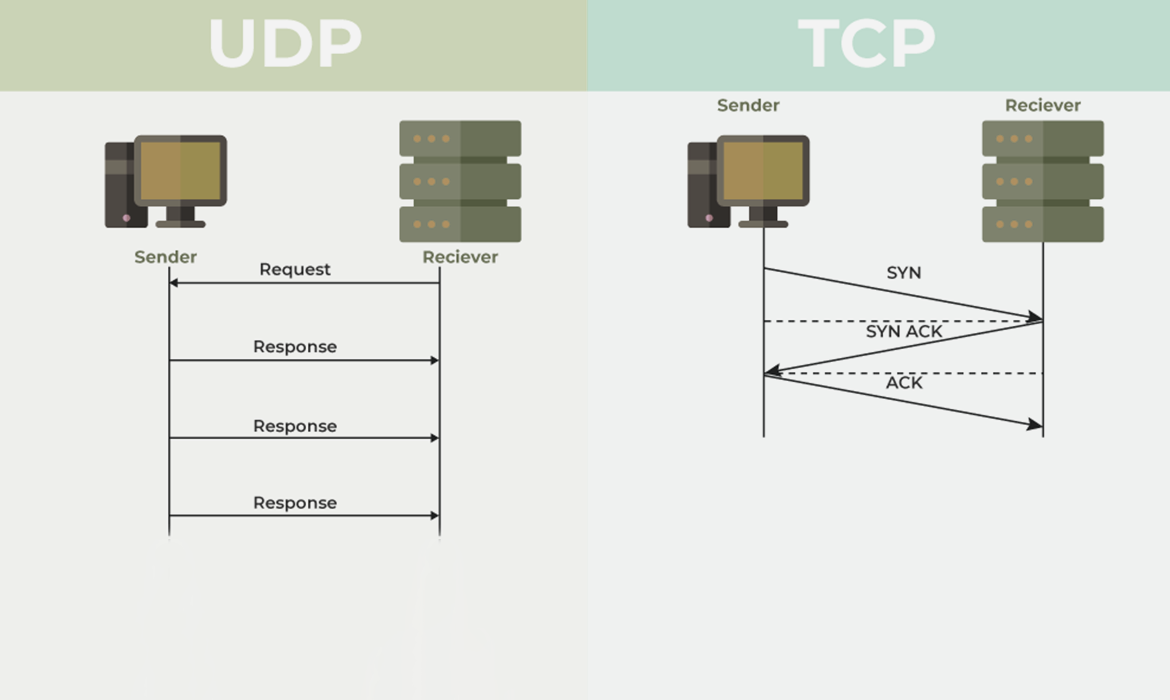
TCP, or Transmission Control Protocol, is like sending a certified letter. When your data travels over the internet, TCP ensures it reaches the destination safely and in the correct order. Every piece of data is broken into packets, and TCP checks that each packet arrives. If a packet gets lost, TCP requests a resend. This makes it highly reliable, which is why it’s used for activities where accuracy is critical, like emails, online banking, and file transfers.
TCP also maintains a connection between sender and receiver until all data is delivered. This “handshake” process guarantees that both ends are ready to communicate, making TCP slower than other protocols but very trustworthy.
What is UDP?
UDP, or User Datagram Protocol, is like sending a postcard. It’s fast and efficient but doesn’t guarantee delivery. Packets may arrive out of order or not at all, but that’s often okay for certain applications. Think of streaming a live video or online gaming. You want speed more than perfection. A few lost frames or minor glitches don’t ruin the experience, but delays would.
Unlike TCP, UDP doesn’t establish a connection before sending data. It’s lightweight and excellent for tasks requiring quick transmission, making it essential for live broadcasts, voice calls, and gaming.
Key Differences Between TCP and UDP
Understanding TCP and UDP is easier when we compare them side by side:
- Reliability: TCP is reliable; UDP is not.
- Connection: TCP establishes a connection; UDP is connectionless.
- Speed: TCP is slower; UDP is faster.
- Use Cases: TCP for emails, file transfers, web browsing; UDP for streaming, gaming, VoIP.
- Data Ordering: TCP ensures packets arrive in order; UDP does not.
These differences make each protocol suitable for specific tasks. Choosing the right one can improve network efficiency and user experience.
How TCP Ensures Data Integrity
TCP uses several mechanisms to keep data safe:
- Sequencing: Each packet is numbered, so the receiver can reorder them correctly.
- Acknowledgments: The receiver confirms receipt of packets, and any missing packets are resent.
- Error Checking: TCP checks for corrupted packets and requests retransmission.
This makes TCP ideal for sensitive or important data, such as financial transactions, file downloads, and emails.
How UDP Prioritizes Speed
UDP keeps things simple and fast:
- No Handshake: UDP sends packets without confirming readiness, reducing delays.
- Minimal Overhead: Less processing is required, making it lightweight.
- Tolerance for Loss: Small losses don’t affect the application much, ideal for video calls or gaming.
By trading reliability for speed, UDP supports applications where delay is more harmful than occasional data loss.
Real-World Examples of TCP
- Web Browsing: When you load a website, TCP ensures all images and text display correctly.
- Email: Sending an email relies on TCP to make sure your message reaches the recipient intact.
- File Transfers: Downloading a file uses TCP to prevent corruption.
In each case, the accuracy and order of data are more important than speed.
Real-World Examples of UDP
- Live Streaming: Watching a live sports game uses UDP for smooth playback.
- Online Gaming: Multiplayer games need speed to maintain real-time interactions.
- Voice Over IP (VoIP): Calls prioritize timeliness over missing packets.
Here, speed is key, and occasional data loss is acceptable.
When to Choose TCP or UDP
Choosing between TCP and UDP depends on your priorities:
- Use TCP when reliability and accuracy matter. Examples: emails, banking, file transfers.
- Use UDP when speed is more critical than perfection. Examples: gaming, video streaming, live broadcasts.
Sometimes, applications even combine both, using TCP for setup and UDP for actual data transfer.
Understanding Ports in TCP and UDP
Ports act like doors for data on a device. TCP and UDP use ports to identify specific services:
- TCP Ports: 80 (HTTP), 443 (HTTPS), 21 (FTP)
- UDP Ports: 53 (DNS), 123 (NTP), 500 (VPN connections)
Each port ensures that data reaches the correct application. This organization is vital for network efficiency and security.
Security Considerations
TCP and UDP have different security implications:
- TCP: Its handshake mechanism makes it easier to filter and secure, but slower connections can be vulnerable to certain attacks.
- UDP: Lack of connection makes it harder to secure, often exploited in DDoS attacks.
Proper network security requires understanding which protocol your applications use and implementing firewalls, encryption, and monitoring accordingly.
Advantages and Disadvantages of TCP
Advantages:
- Reliable data delivery
- Error checking and correction
- Ordered data transmission
Disadvantages:
- Slower speed
- Higher overhead
- Not ideal for real-time applications
Advantages and Disadvantages of UDP
Advantages:
- Fast and efficient
- Low overhead
- Ideal for time-sensitive applications
Disadvantages:
- No guarantee of delivery
- Packets can arrive out of order
- Not suitable for critical data
FAQs About TCP and UDP
1. Can TCP and UDP be used together?
Yes, some applications use TCP for control messages and UDP for fast data transfer.
2. Why is UDP faster than TCP?
UDP skips handshakes and error-checking, allowing quicker data transmission.
3. Is TCP safer than UDP?
TCP is more reliable, but both can be secured with encryption and firewalls.
4. Which is better for video calls?
UDP is preferred due to its low latency and faster speed.
5. Can TCP handle real-time applications?
Yes, but it may introduce delays due to its reliability mechanisms.
6. What happens if UDP packets are lost?
Applications tolerate minor loss, but missing data may cause glitches or artifacts.
Conclusion
Understanding TCP and UDP is essential for anyone who uses the internet. TCP prioritizes reliability, while UDP focuses on speed, and knowing the differences helps you choose the right protocol for your needs. Whether you’re streaming videos, gaming online, or sending emails, these protocols work behind the scenes to keep your digital world running smoothly. By recognizing their strengths and limitations, you can make smarter decisions in networking, software development, and cybersecurity. Next time you enjoy a seamless video call or fast file download, you’ll know TCP and UDP are the unsung heroes making it possible.